Automation tools and frameworks are the backbone of modern engineering, QA, and operations, so you probably searched this because you want to find, evaluate, or build a reliable automation stack. Your intent is mostly informational with practical and transactional elements, you want usable advice you can apply immediately. In my experience helping teams move from ad hoc scripts to robust automation pipelines, success comes from matching the right tools to the job, keeping operations secure, and designing for maintainability. This guide explains what automation tools and frameworks are, why they matter, how to choose and implement them step by step, real code examples, best practices, and the legal and security trade-offs you must consider.
What automation tools and frameworks are, and why they matter
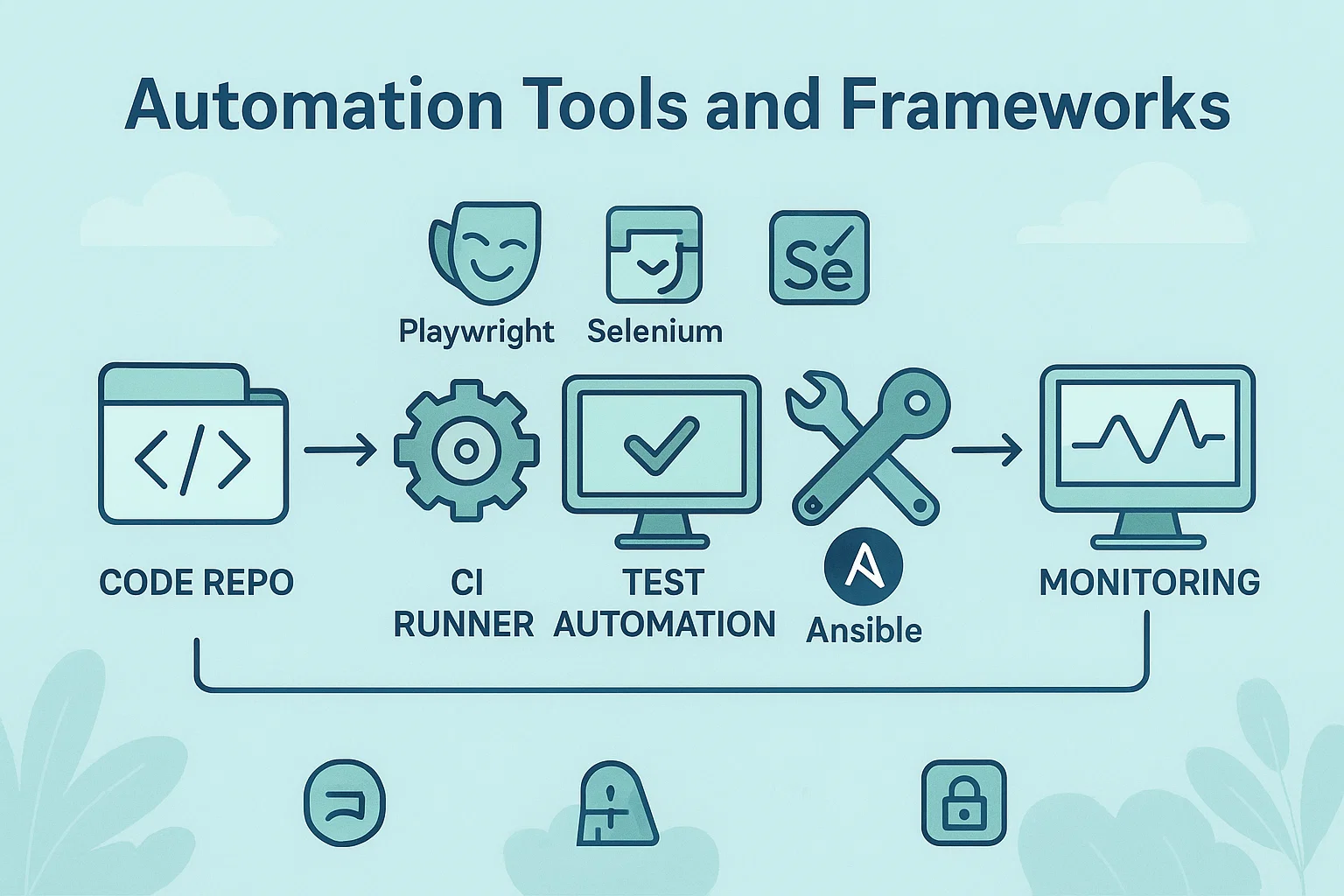
Automation tools are software that execute repeatable tasks without manual intervention, while automation frameworks are the structured conventions, libraries, and patterns you use to build those automated workflows. Use cases span test automation, CI/CD pipelines, infrastructure as code, configuration management, robotic process automation, and security testing.
A short history and context
Automation started as simple shell scripts, then evolved with frameworks that add structure, reporting, and reuse. Tools like browser automation libraries, configuration managers, and CI runners let teams move from fragile one-off scripts to repeatable, auditable workflows. Selenium and Playwright set the standard for browser automation, while Ansible and similar frameworks handle provisioning and configuration at scale. Selenium+2Playwright+2
Why it matters to you
Automation saves time, reduces human error, and lets teams release faster. But poorly chosen tools create brittle tests, hidden costs, and security gaps. Framing your automation strategy around goals, reliability, and observability is essential, otherwise automation becomes technical debt.
“Selenium automates browsers and provides a WebDriver standard so browser scripts are portable across engines,” paraphrased to highlight how a browser automation tool fits into an automation stack. Selenium
How to choose and implement automation tools and frameworks, step by step
Below is a pragmatic workflow you can follow, with code samples to get you started.
High-level decision flow
- Define the job: end-to-end test, infra provisioning, repetitive admin task, or RPA.
- Choose categories: browser automation, infra automation, CI/CD orchestration, security automation.
- Shortlist candidates by documented features, community, and security controls.
- Run a proof-of-concept for 2–3 tools, measure throughput, flakiness, and maintenance cost.
- Automate, observe, iterate.
Step 1 — Define clear automation outcomes
Write a one-paragraph goal for each automation, for example, “Run cross-browser smoke tests on every merge, fail fast if login breaks.” Goals keep tool choice grounded.
Step 2 — Pick the right tool category
- For browser and UI: Playwright or Selenium. They provide API-driven automation across browsers and platforms. Playwright+1
- For configuration and orchestration: Ansible, Terraform, or similar frameworks. They model desired state and scale. Ansible Documentation
- For CI/CD: Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, or cloud pipelines to run jobs, record results, and trigger deployments.
- For RPA: platforms that support UI automation, credential management, and governance.
Step 3 — Proof-of-concept and acceptance criteria
Run a short POC that covers:
- Reliability, how often tests fail for environmental noise.
- Speed and concurrency, how pipelines parallelize.
- Observability, logs, artifacts, and alerts.
- Cost and maintenance effort.
Step 4 — Implement a basic pipeline (example)
Here’s a minimal example showing Playwright tests triggered from a simple Node.js script, and a Python snippet for running an Ansible playbook.
// node: run a Playwright test programmatically
// requires: npm install playwright
const { chromium } = require('playwright');
(async () => {
let browser;
try {
browser = await chromium.launch();
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto('https://example.com', { waitUntil: 'domcontentloaded' });
const title = await page.title();
console.log('Page title:', title);
// add assertions and reporting hooks here
} catch (err) {
console.error('Test error', err);
process.exitCode = 1;
} finally {
if (browser) await browser.close();
}
})();
Explanation: Run Playwright tests in isolated workers and capture artifacts for debugging. Playwright supports multiple browsers from one API. Playwright
# python: run an Ansible playbook programmatically via ansible-runner
# requires: pip install ansible-runner
import ansible_runner
try:
result = ansible_runner.run(playbook='site.yml', inventory='hosts.ini')
print('Status:', result.status)
print('RC:', result.rc)
except Exception as e:
print('Ansible run failed', e)
Explanation: Ansible playbooks declaratively manage remote state, ideal for config and deployment tasks, run from CI or orchestration controllers. Ansible Documentation
Best practices, recommended tools, and pros & cons
Core best practices
- Define ownership: every automation needs an owner for maintenance.
- Version everything: store playbooks, tests, and configs in source control.
- Use human-in-the-loop for high-risk steps: approvals before prod changes.
- Measure flakiness and fix root causes: flaky tests hide real bugs.
- Secure credentials: use vaults or secret managers, never store secrets in plain text.
Recommended tooling by purpose
- UI testing: Playwright, Selenium. Playwright+1
- Configuration management: Ansible, Terraform for infra as code. Ansible Documentation
- CI/CD orchestration: GitHub Actions, Jenkins, GitLab CI, cloud pipelines.
- Security automation: OWASP cheat sheets and ZAP automations for continuous scanning. OWASP Cheat Sheet Series+1
Pros and cons
- Pros: faster releases, consistent environments, repeatable testing, and audit trails.
- Cons: upfront engineering cost, maintenance burden, and potential security exposure if credentials or access controls are mishandled.
“Platform docs emphasize automation reduces manual effort while requiring governance to avoid unsafe changes,” paraphrased from vendor and standards guidance, showing why governance matters. Ansible Documentation+1
Challenges, legal and ethical considerations, and troubleshooting
Common challenges and fixes
- Flaky tests: isolate environment differences, add retries with backoff, and stabilize fixtures.
- Slow pipelines: parallelize tests, cache dependencies, and split smoke vs full regressions.
- Secrets exposure: rotate keys, use short-lived tokens, and integrate secret vaults.
Legal, compliance, and safety checklist
- Respect access boundaries: only automate against infrastructure you own or are authorized to manage.
- Data protection: if automation touches personal data, implement data minimization, and honor subject rights under relevant privacy laws.
- Intellectual property and scraping: avoid unauthorized scraping of third-party services, and prefer official APIs.
- Audit and logging: keep change logs and approval records to support investigations.
Security guidance
Use OWASP CI/CD and automation cheat sheets to harden pipelines, run security scans as part of your automation, and treat automation runners as production systems that require patching and monitoring. OWASP Cheat Sheet Series+1
FAQs
What is automation tools and frameworks?
Automation tools and frameworks refer to the software and structured patterns used to automate tasks like testing, deployments, configuration, and repetitive business processes. They combine libraries, runners, and conventions to create reliable automation pipelines.
Which framework is best for browser automation?
Playwright and Selenium are the leading choices. Playwright offers modern APIs and reliability, while Selenium provides a mature WebDriver standard for cross-browser compatibility. Playwright+1
Do I need to code to use automation tools and frameworks?
Some platforms offer low-code interfaces, but most reliable automation requires scripting to handle edge cases, assertions, and integrations. Knowing at least one scripting language helps.
How do I secure automation pipelines?
Store secrets in a vault, use least privilege for runners, scan pipelines for secrets, and apply CI/CD hardening guidance from security best practices. OWASP Cheat Sheet Series
Can automation replace manual testing entirely?
No, automation complements manual testing. Use automation for repeatable checks and manual testing for exploratory and usability tasks.
How do I measure ROI from automation?
Track cycle times, defect escape rate, mean time to recovery, and hours saved on repetitive tasks. These metrics show automation value over time.
What are common pitfalls when adopting automation tools and frameworks?
Common pitfalls include unclear ownership, brittle tests, lack of observability, and underestimating maintenance costs.
How do I start small with automation?
Pick a high-value, low-complexity workflow, automate it fully, measure results, then expand iteratively.
Conclusion and call to action
Key takeaways: adopt automation tools and frameworks that match your goals, prototype before committing, secure credentials and pipelines, and assign clear ownership. Automation pays off when it is reliable, observable, and maintainable. If you want, I can generate a starter repository with a Playwright smoke test, an Ansible playbook, and CI configuration tailored to your stack. Try one small automation today, measure the benefit, and expand from there.